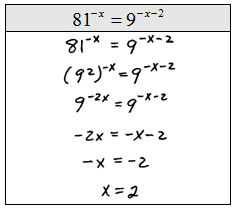In this section, we will make use of what we have learned about exponential functions to solve equations.
Make use of the above property if you are able to express both sides of the equation in terms of the same base.
Step 1: Express both sides in terms of the same base.
Step 2: Equate the exponents.
Step 3: Solve the resulting equation.
Solve.
It is not always the case that we will be able to express both sides of an equation in terms of the same base. For this reason we will make use of the following property.
Make use of the above property if you are unable to express both sides of the equation in terms of the same base.
Step 1: Isolate the exponential and then apply the logarithm to both sides.
Step 2: Apply the power rule for logarithms and write the exponent as a factor of the base.
Step 3: Solve the resulting equation.
Solve.
When solving exponential equations and using the above process, the rule of thumb is to choose the common logarithm unless the equation involves the natural base
e. We choose these because there is a button for them on the calculator. However, we could certainly choose any base that we wish; this is the basis for the derivation of the change of base formula.
YouTube Videos: